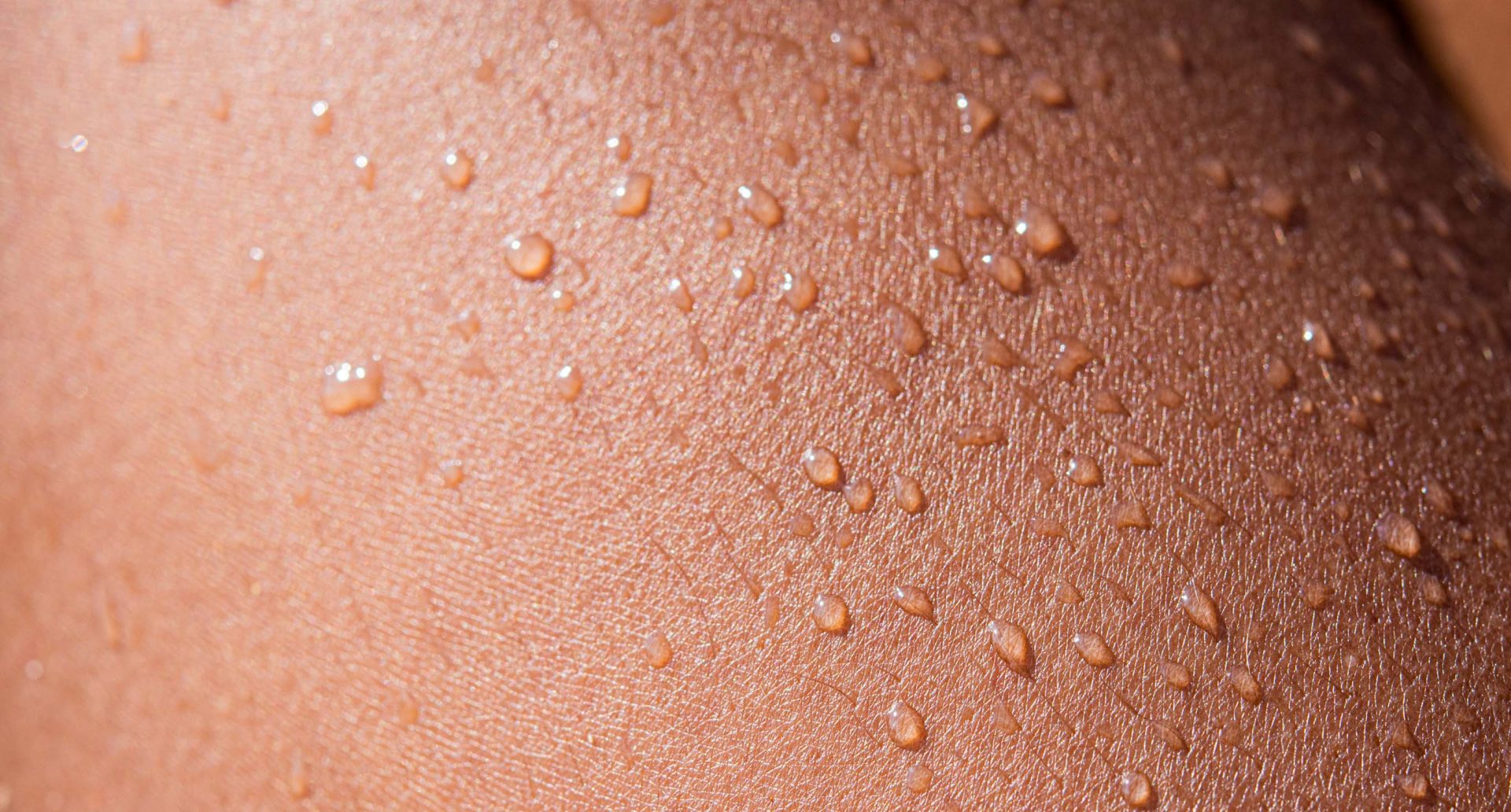
In their article, Robert Ornstein, PhD, and David Sobel, MD, explore the numerous health benefits associated with heat exposure, particularly focusing on the effects of sauna bathing. Research has shown that brief exposure to high temperatures, such as in saunas, can trigger a range of beneficial physiological changes. These include the release of stress hormones, increased heart rate and respiration, and a rise in body temperature, which together help to relax muscles, relieve pain, and even promote a sense of euphoria. One notable study highlighted by the authors found that sauna use led to a doubling of beta-endorphin levels in the blood, which can reduce pain and induce feelings of well-being. Furthermore, sauna bathing may help reduce stress hormones, enhance serotonin production, and improve sleep patterns, making it a relaxing pre-sleep activity.
Additionally, the authors discuss the potential immune-boosting effects of sauna use. Regular sauna bathing has been linked to a reduced frequency of colds and infections in children, likely due to the way the heat stimulates the body in a manner similar to fever, enhancing the immune system’s ability to fight off germs. The article also mentions that sauna use can contribute to calorie burning and heart conditioning, much like exercise. By inducing sweating, which is an active response to heat, sauna bathing burns calories and may improve cardiovascular health. Overall, the article highlights how sauna use can provide a range of benefits, from enhancing relaxation and sleep quality to boosting immune function and supporting physical fitness. These insights suggest that infrared therapy, through its ability to induce heat in the body, could be a valuable tool for improving overall health and well-being.